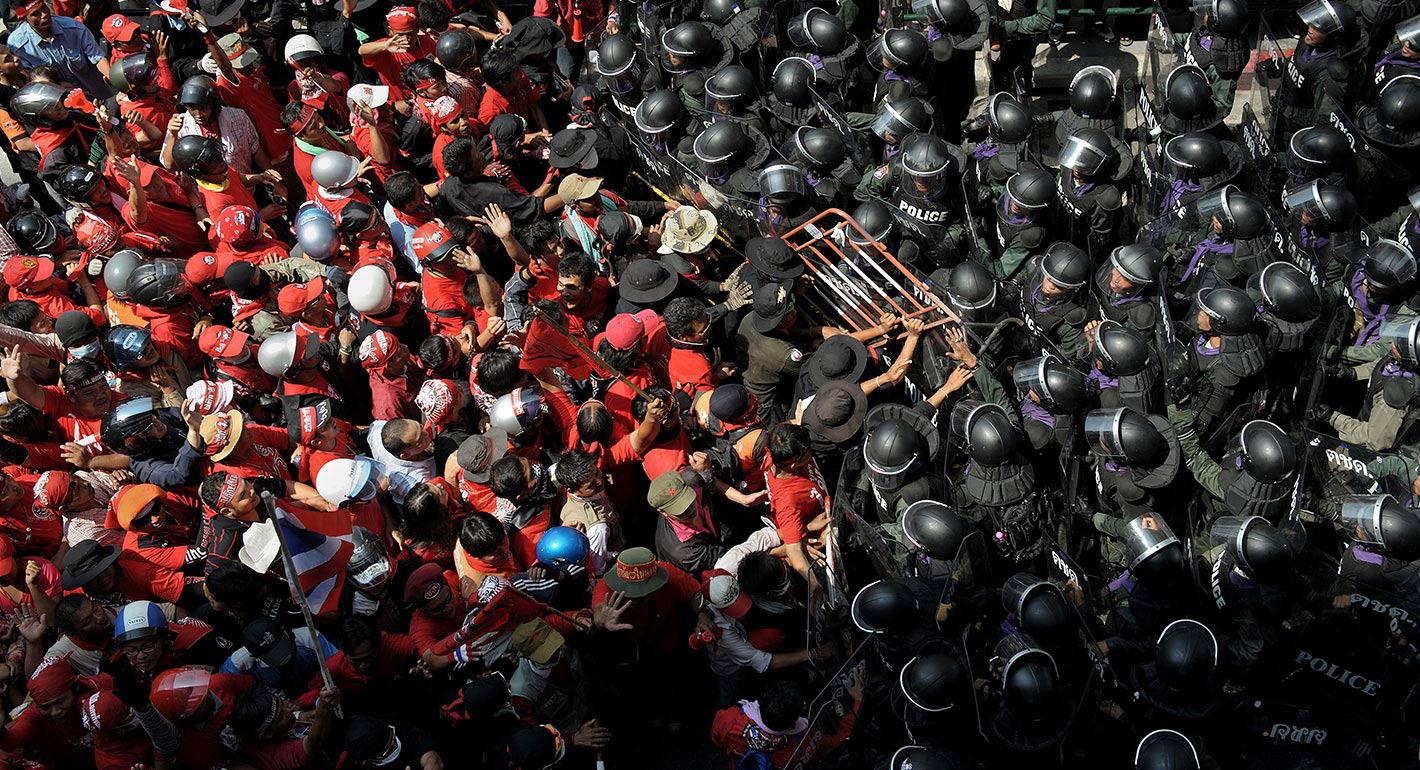
A Closer Look at the Pros and Cons of Direct Democracy
Explore the advantages and disadvantages of direct democracy. Learn about the pros and cons of this political system.

Direct Democracy, Trust, and Representation: Exploring the Pros and Cons in Contemporary Governance and Politics
In the realm of governance and politics, the concept of direct democracy stands as a prominent alternative to representative systems. In an era dominated by a constant influx of political news, such discussions are more relevant than ever. This blog delves into the potential benefits and drawbacks of direct democracy, particularly in the context of trust and representation. We will also touch upon its impact on various political aspects such as upcoming political events, political campaign strategies, state and world politics, and international political news.
Direct Democracy: A Brief Overview
Direct democracy is a form of government in which citizens have the power to make decisions on important issues directly, without relying on elected representatives. Instead of entrusting a small group of individuals with legislative authority, the citizens themselves participate in decision-making processes through referendums, initiatives, and other mechanisms.
Benefits of Direct Democracy
Enhanced Civic Engagement: Direct democracy encourages citizens to actively engage in political matters. By participating in decision-making processes, people become more informed and invested in their government, leading to a more politically aware and engaged population.
Increased Accountability: With direct democracy, elected officials are held directly accountable for their actions and decisions. This heightened accountability can lead to more responsible governance as politicians know that their constituents can directly challenge their decisions.
Responsive to Public Will: Direct democracy ensures that policies and decisions align closely with the will of the people. This can lead to policies that better represent the diverse interests and values of the population.
Decentralization: Direct democracy can foster decentralization, allowing local communities to make decisions that are tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
Drawbacks of Direct Democracy
Complexity and Inefficiency: The direct democratic process can be complex, time-consuming, and inefficient, particularly for complex issues that require nuanced understanding and deliberation.
Potential for Majority Tyranny: Direct democracy may lead to the "tyranny of the majority," where minority rights are overlooked or marginalized. This can be especially problematic in diverse societies.
Vulnerability to Populism: Direct democracy can be susceptible to populism, where decisions are driven by emotion and short-term popularity rather than long-term, well-considered policies.
Lack of Expertise: Citizens may not always have the expertise or information required to make informed decisions on complex issues, potentially leading to suboptimal outcomes.
Trust and Representation in Direct Democracy
One of the critical aspects of direct democracy is the trust it places in the collective wisdom of the people. It assumes that citizens are best equipped to make decisions about their governance. However, this trust can also be a double-edged sword.
Pros of Trust and Representation in Direct Democracy
Empowerment: Direct democracy empowers citizens by giving them a direct say in political matters. This can foster a sense of ownership and trust in the political process.
Transparency: The transparency inherent in direct democracy can enhance trust in government. When decisions are made openly and with public involvement, suspicions of corruption or favoritism can be reduced.
Cons of Trust and Representation in Direct Democracy
Voter Apathy: Ironically, the trust placed in citizens can sometimes lead to voter apathy. When people believe their voices don't matter in a complex direct democracy, they may disengage from politics altogether.
Risk of Polarization: Trusting citizens to make decisions can lead to polarization when deeply divided populations vote on contentious issues, potentially exacerbating divisions rather than finding common ground.
Limited Representation: While direct democracy emphasizes citizen participation, it may not guarantee equal representation for minority groups, leading to concerns about fairness and equity.
Impact on Political News, Campaign Strategies, and Political Events
Direct democracy has significant implications for political news, campaign strategies, and upcoming political events:
Political News Today: Direct democracy initiatives and referendums often make headlines in political news today. Citizens are eager to stay informed about the latest developments in their jurisdiction, as these decisions directly affect their lives.
Political Campaign Strategies: Politicians and interest groups must adapt their campaign strategies when direct democracy is in play. They need to engage directly with voters, educate them on complex issues, and rally support for their positions.
Upcoming Political Events: Direct democracy can lead to a flurry of upcoming political events, such as referendums and ballot measures. These events become focal points of political discourse and mobilization efforts.
State and World Politics: The implementation of direct democracy can vary from state to state, influencing state politics differently. It also has implications for how countries interact in the international political arena.
International Political News: When direct democracy results in significant policy shifts, it can attract international attention and become part of world politics news, especially if the decisions have global repercussions.
The Evolution of Direct Democracy
Direct democracy is not a new concept, but its implementation has evolved over time. While ancient Athens is often cited as an early example of direct democracy, contemporary forms of direct democracy have adapted to the complexities of modern societies. Here are some key ways in which direct democracy has evolved:
Technological Advancements: The digital age has revolutionized the way direct democracy operates. Online voting, digital petitions, and social media platforms have made it easier for citizens to participate in decision-making processes.
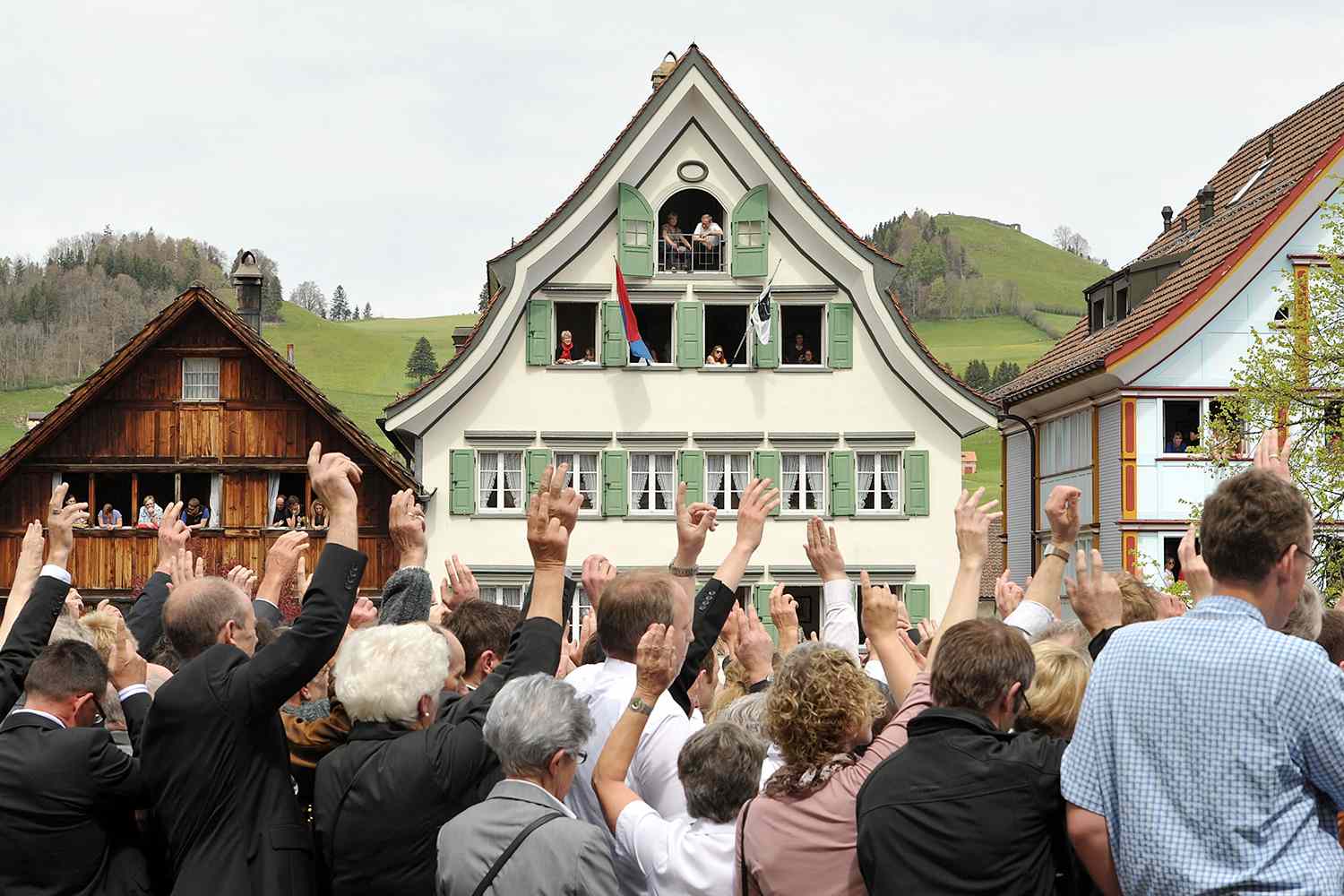
Hybrid Models: Many countries have adopted hybrid models that combine elements of both direct and representative democracy. For example, Switzerland has a strong tradition of direct democracy, but it also has elected representatives who handle day-to-day governance.
Use of Experts: Some direct democracy systems incorporate advisory committees or expert panels to provide information and analysis to voters. This helps address the challenge of voter expertise in complex policy areas.
Constitutional Safeguards: To prevent the potential drawbacks of direct democracy, some countries have implemented constitutional safeguards that protect minority rights and ensure that certain decisions remain the purview of elected representatives.
Contemporary Examples of Direct Democracy
To better understand the impact of direct democracy, let's look at some contemporary examples:
Switzerland: Switzerland is often regarded as a model of direct democracy. Swiss citizens can propose referendums on various issues, from tax policies to immigration. This system has fostered a culture of political engagement and consensus-building.
California, USA: California allows citizens to initiate ballot measures on a wide range of issues. These measures can directly amend the state's constitution or enact new laws. However, the sheer volume of ballot measures has led to concerns about voter fatigue and the unintended consequences of some decisions.
Brexit Referendum (UK): The 2016 Brexit referendum in the United Kingdom is a prominent example of direct democracy. The decision to leave the European Union was put directly to the people. The outcome had far-reaching consequences, including political turmoil and economic uncertainty.
Initiative and Referendum in US States: Many U.S. states have initiative and referendum processes that allow citizens to propose and vote on laws and constitutional amendments. These processes have been used to legalize recreational marijuana, expand Medicaid, and impose term limits on politicians.
The Future of Direct Democracy
The future of direct democracy is shaped by ongoing debates and innovations in governance and politics. Here are some key considerations for the future:
Technology and Accessibility: As technology continues to advance, direct democracy may become more accessible and inclusive. Mobile apps and online platforms could simplify the process of citizen participation.
Education and Information: To address the challenge of informed decision-making, efforts to educate citizens about complex issues will be crucial. Providing unbiased information and facilitating deliberative discussions can enhance the quality of direct democracy.
Balancing Trust and Representation: Striking the right balance between trust in citizens and the need for expert governance will remain a central challenge. Constitutional safeguards and mechanisms to ensure minority rights will continue to be debated.
Global Implications: Direct democracy decisions on issues such as climate change, trade, and international relations can have global repercussions. These decisions may require new forms of international cooperation and diplomacy.
Evolving Political Campaign Strategies: Political campaigns will need to adapt to direct democracy. Campaigns will focus on grassroots mobilization, issue advocacy, and educating voters on referendum topics.
Direct democracy presents both opportunities and challenges in contemporary governance and politics. Its evolution is influenced by technological advancements, the need for informed decision-making, and the quest for a balance between trust in citizens and effective governance. As we continue to engage in political discourse, it is essential to critically examine and shape the future of direct democracy, keeping in mind its impact on state and world politics, international political news, upcoming political events, and political campaign strategies.
What's Your Reaction?